SEN Support
Special educational provision
The SEND Code of Practice Chapter 6 explains what schools need to do to support children with SEN.
All children and young people are entitled to an appropriate education, that enables them to achieve their best, become confident individuals living fulfilling lives and make a successful transition into adulthood. All pupils should have access to a broad and balanced curriculum and lessons should be planned to address potential areas of difficulty and remove barriers to pupil achievement. This means that schools must do everything they can to meet children and young people's SEN and make sure children and young people with SEN can engage in the activities of the school.
Under the Equality Act 2010, all schools have duties towards individual disabled children and young people. They must make reasonable adjustments to prevent them from being disadvantaged, prevent discrimination and promote equality of opportunity.
Schools should have a clear approach to identifying and responding to SEN. They must have a teacher responsible for co-ordinating SEN provision (the SENCO) and inform parents when they are making special educational provision for a child.
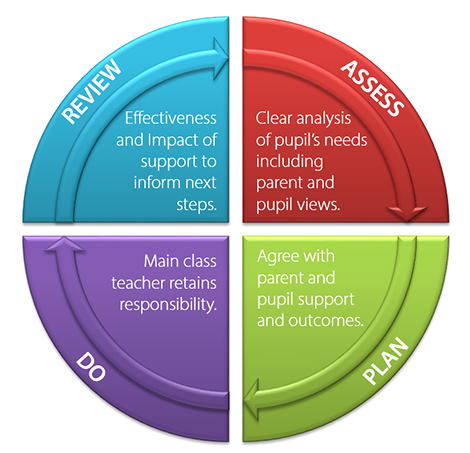
Where a pupil is identified as having SEN, schools should put effective special educational provision in place through a graduated approach. The graduated approach is a four-part cycle of:
- assess
- plan
- do
- review
Parents should have clear information about the impact of the support and interventions provided, and be involved in planning next steps.